In recent months, a concerning trend has emerged in the United States: an increase in cases of a rare, paralyzing illness linked to a specific virus. Enterovirus D68 (EV-D68), a member of the enterovirus family, has been associated with a spike in Acute Flaccid Myelitis (AFM), a condition that can lead to sudden muscle weakness and paralysis. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have confirmed 13 cases of AFM this year, raising alarms about the potential for further spread and the need for public awareness and action.
What is Enterovirus D68?
Enterovirus D68 is a virus that primarily affects the respiratory system. First identified in 1962, EV-D68 has been known to cause outbreaks of respiratory illness, particularly in children. Unlike many other enteroviruses, EV-D68 is distinct due to its ability to cause severe respiratory issues, including wheezing and difficulty breathing.
Historically, EV-D68 outbreaks have been sporadic, with notable surges occurring every few years. The virus gained increased attention in 2014 when a significant outbreak in the U.S. led to a rise in severe respiratory illness among children. Recent data suggests that EV-D68 is once again becoming a major concern, with evidence linking it to an increase in cases of AFM.
Understanding Acute Flaccid Myelitis (AFM)
Acute Flaccid Myelitis is a rare but serious neurological condition that primarily affects children. It is characterized by sudden onset of muscle weakness, often accompanied by other symptoms such as facial droop, difficulty swallowing, and in severe cases, respiratory failure. AFM can result from a range of causes, but viral infections, including those caused by EV-D68, have been implicated in many cases.
Diagnosing AFM involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is often used to assess spinal cord damage, while lumbar puncture (spinal tap) may be performed to analyze cerebrospinal fluid. Despite these diagnostic tools, identifying AFM can be challenging, as its symptoms overlap with other conditions.
The Link Between Enterovirus D68 and AFM
Research has shown a strong correlation between EV-D68 infections and the onset of AFM. Several studies have demonstrated that children with AFM often have a history of recent respiratory illness, which is consistent with EV-D68 infection. The virus appears to enter the body through the respiratory tract and can, in rare cases, invade the nervous system, leading to the development of AFM.
Recent outbreaks have provided further evidence of this link. In 2018, an outbreak of EV-D68 coincided with a significant increase in AFM cases, prompting researchers to investigate the relationship more closely. Findings suggest that while not all EV-D68 infections lead to AFM, the virus is a significant risk factor for the condition.
Current Statistics and Data
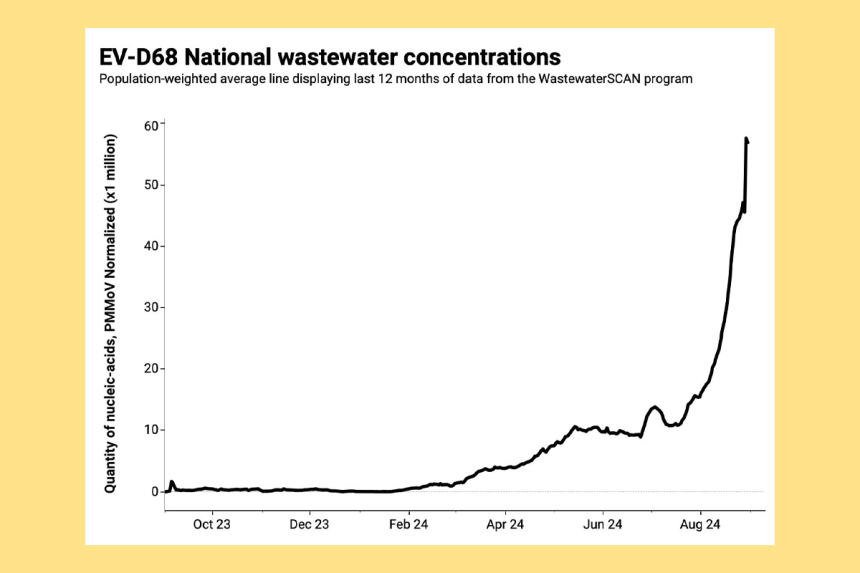
The CDC’s recent report highlights a concerning trend in AFM cases. As of this year, 13 cases have been confirmed, with more under investigation. Wastewater data has become an important tool in tracking the spread of enteroviruses, including EV-D68. This data provides insights into the prevalence of the virus in different communities, helping public health officials anticipate potential outbreaks.
The role of the CDC in monitoring and responding to these cases is crucial. By analyzing data and coordinating with state and local health departments, the CDC helps manage the response to AFM and EV-D68 outbreaks, working to mitigate the impact on affected communities.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of AFM
Early detection of AFM is critical for effective management. Symptoms typically begin with mild respiratory illness, followed by sudden muscle weakness. Parents and caregivers should be vigilant for signs such as difficulty moving limbs, facial droop, and trouble swallowing.
Diagnostic challenges arise due to the rarity of AFM and its similarity to other conditions. Comprehensive evaluation by a neurologist and the use of advanced imaging techniques are essential for an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment and Management of AFM
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for AFM. Management focuses on supportive care, including physical therapy to help regain muscle strength and function. Rehabilitation can be intensive and requires a multidisciplinary approach involving neurologists, physical therapists, and occupational therapists.
Research is ongoing to find more effective treatments and potentially a vaccine for EV-D68. Advances in medical research offer hope for better management strategies in the future.
Prevention and Public Health Measures
Preventing EV-D68 infection involves standard hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. Public health recommendations emphasize the importance of these measures, especially during outbreaks.
Vaccination research is underway to explore the potential for an effective vaccine against EV-D68. While no vaccine is currently available, ongoing research aims to develop preventive solutions to reduce the incidence of EV-D68 and associated conditions like AFM.
Impact on Families and Communities
The emotional and psychological impact of AFM on families is profound. The sudden onset of paralysis and the uncertainty surrounding recovery can be overwhelming for affected individuals and their loved ones. Support from healthcare providers and community organizations is vital in helping families cope with the challenges of AFM.
Communities play a crucial role in supporting affected families and raising awareness about AFM and EV-D68. Increased public knowledge and engagement can contribute to better preparedness and response during outbreaks.
Looking Forward: Future Research and Directions
The future of managing and preventing AFM and EV-D68 relies on continued research and vigilance. Ongoing studies aim to improve our understanding of the virus and its effects, with the goal of developing effective treatments and preventive measures.
The potential for future outbreaks underscores the importance of maintaining a robust public health response and investing in research. Collaboration among scientists, healthcare professionals, and public health officials is essential to address these challenges effectively.
Conclusion
The recent increase in cases of AFM linked to Enterovirus D68 highlights the need for continued attention and action. Understanding the connection between the virus and the rare neurological condition is crucial for effective management and prevention. By staying informed and following public health recommendations, we can work together to reduce the impact of EV-D68 and protect vulnerable populations.